Cast steel valves are vital components in industrial flow control, delivering durability, strength, and performance across demanding applications. Their robust construction enables them to withstand conditions such as high pressures, extreme temperatures, and corrosive environments. This article examines what cast steel valves are, their types, advantages, and available grades.
What Are Cast Steel Valves?
The manufacture of cast steel valves entails pouring molten steel into molds that define the shape of the valve body and bonnet. This process allows engineers to produce complex geometries with consistent mechanical properties, making it easy to scale up valves to much larger diameters while still maintaining performance integrity.
Casting vs Forging
- Casting is ideal for valve bodies with intricate internal passageways, larger diameters, or when economic scalability is important. The manufacture of large-bore valves (24” and above) is almost exclusively via casting because forging such components would be technically challenging and prohibitively expensive.
- Forging provides a finer grain structure and higher toughness, thus making it ideal for small-diameter, high-integrity applications. However, in larger valves where weight and size are factors, casting remains the most practical method.
Key Performance Characteristics
- Strength and Pressure Containment: Cast steel valves can withstand ANSI/ASME pressure classes ranging from Class 150 up to Class 2500 (20 bar to over 420 bar). This wide range makes them suitable for both low-pressure distribution and extremely high-pressure transmission systems.
- High-Temperature Capability: Depending on the alloy grade, cast steel valves can handle operating temperatures from cryogenic service (as low as –196°C / –320°F) up to approximately 593°C (1100°F) in chrome-moly or alloy steel grades. Additionally, austenitic stainless steels extend service in corrosive environments at elevated temperatures.
- Toughness: Cast valves maintain mechanical strength and impact resistance, even under shock loads, vibration, or fluctuating pipeline stresses. This is critical in refineries, offshore rigs, and high-cycle power plants.
- Leak-Tight Sealing: Precision machining of seating surfaces, combined with hardfacing (e.g., Stellite overlays), ensures repeatable tight shutoff and minimal leakage even under severe cyclic or erosive service.
- Adaptability: Cast steel valves can consist of several alloys, making them suitable for diverse fluids, including hydrocarbons, acids, slurries, and water.
Types of Cast Steel Valves
Different valve designs are available to suit specific service requirements. The main types include:
Gate Valves
Gate valves primarily serve for isolation, where the goal is either full flow or complete shutoff. They provide bi-directional sealing, with a straight-through bore that results in negligible pressure drop when the valve is fully open.
The closure element is typically a wedge-shaped gate that moves linearly perpendicular to the flow. Designs include solid wedge, flexible wedge, and split wedge types, with selection depending on thermal cycling or sealing requirements.
Stem configurations (rising vs. non-rising) determine the visual indication of valve position. The sealing surfaces are hard-faced with alloys such as Stellite to resist wear and galling.
- Applications: Critical for isolation in oil and gas transmission pipelines, refinery process units, and power generation main steam lines where bubble-tight shutoff is mandatory.
Globe Valves
Globe valves are ideal for throttling and flow regulation, providing fine control over flow rates. The disc moves in a linear path against a stationary seat, thus creating a tortuous flow path that offers high control resolution. Variants include Z-body, Y-pattern, and angle globe designs. Disc shapes (plug, needle, composition) are selected based on required throttling accuracy and pressure drop considerations.
Globe valves typically exhibit higher pressure loss compared to gate valves, but their ability to handle frequent operation and precise control makes them indispensable. At QRC Valves, one of the most popular offerings is the Chaoda Cast Globe valve, as seen in the image below.
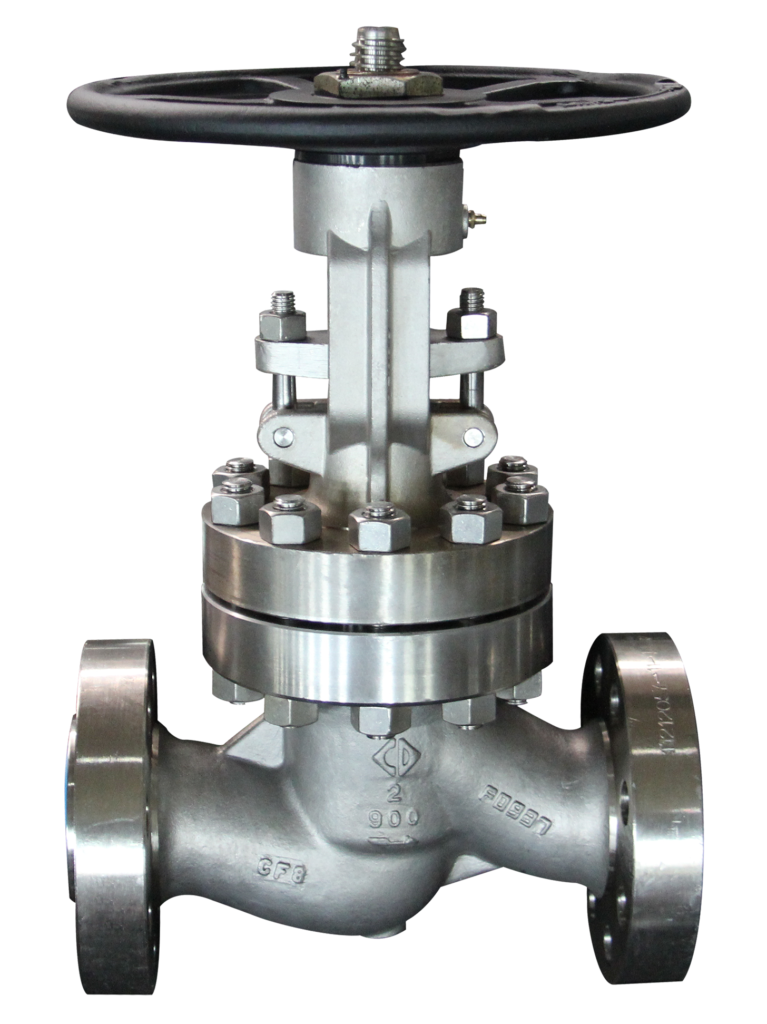
- Applications: Used in steam control for power plants, boiler feedwater regulation, chemical dosing, and other process systems requiring flow modulation.
Check Valves
Check valves automatically prevent backflow and protect upstream equipment such as pumps, compressors, and turbines. Designs include swing check (hinged disc), lift check (disc moves vertically), and tilting-disc check (pivoted for smoother closure). While engineering considerations involve cracking pressure, closing speed, and minimization of water hammer effects. Seats are often overlaid with wear-resistant alloys to extend service life under repetitive cycling. Our DSI Cast Steel Valves include gate, globe, and check valves, highlighted in the image below.

- Applications: Common in water distribution networks, hydrocarbon pipelines, and high-pressure process systems to maintain unidirectional flow and system integrity.
Ball Valves
Ball valves enable rapid quarter-turn shutoff with very low flow resistance when open.
The closure element is a precision-machined spherical ball with a through bore, operated by a stem that rotates 90 degrees. Seats typically consist of soft materials (PTFE, reinforced polymers) or metal-seated for high-temperature and abrasive service. The design of cast steel ball valves is suitable for higher sizes and pressures than typical forged ball valves.
Engineering aspects include floating-ball vs. trunnion-mounted designs, fire-safe construction, and anti-blowout stems.
- Applications: Used for emergency isolation, hydrocarbon transfer lines, gas distribution, and chemical processing because fast operation and tight shutoff are essential.
Advantages of Cast Steel Valves
Cast steel valves offer multiple benefits over alternative valve designs:
- Durability: Their robust body construction makes them ideal for systems exposed to high pressures, rapid pressure fluctuations, and thermal cycling.
- High-Temperature Capability: Depending on alloy grade, cast steel valves are capable of operating reliably from cryogenic service to above 1000°F.
- Serviceability: Unlike fabricated valves, cast steel valves are repairable. Seats, discs, and stems can be replaced or refurbished without discarding the entire valve.
- Large Size Availability: Casting allows the manufacture of valves up to 60” or more, which is impractical with forged construction.
- Economic Viability: Casting lowers the cost per unit when producing large and complex valve geometries, balancing cost with performance.
Grades of Cast Steel Valves
Selecting the right steel grade is critical for ensuring reliable service. Common grades include:
- WCB (Carbon Steel, ASTM A216): General-purpose material, used in water, oil, and gas service. Cost-effective and capable of handling moderate temperatures.
- LCC (Low-Temperature Carbon Steel, ASTM A352): Engineered to withstand temperatures as low as –46°C (–50°F). Hence, essential for cryogenic and arctic operations.
- CF8M (Stainless Steel, ASTM A351, 316 Equivalent): Offers corrosion resistance in aggressive chemical and chloride-containing environments. As a result, they are ideal for offshore and chemical processing industries.
- Chrome-Moly Alloys (e.g., WC6, WC9): Enhanced strength and creep resistance at elevated temperatures, typically used in high-pressure steam service.
- Duplex Stainless Steels: Provide resistance to stress corrosion cracking and erosion, hence duplex steels are ideal for offshore and subsea pipelines.
Applications of Cast Steel Valves
The engineering versatility of cast steel valves makes them suitable across a wide spectrum of industries and service environments. Their design adaptability, pressure class range, and availability in multiple grades allow engineers to specify them for mission-critical applications where safety and reliability are top priority.
Oil & Gas (Upstream, Midstream, Downstream)
Cast steel gate and check valves are mainstays in wellhead isolation, crude oil transport pipelines, gathering systems, and refinery process units. Moreover, offshore platforms use LCC and stainless steel grades to handle low-temperature and corrosive environments. High-pressure gas compression facilities also rely on Class 900–2500 valves for secure containment.
Power Generation
In fossil-fuel and nuclear plants, cast steel globe valves regulate superheated steam lines, while gate valves isolate turbine bypasses. Moreover, chrome-moly grades (WC6, WC9) are used for high-temperature, high-pressure boiler service. Check valves protect feedwater pumps from reverse flow, thus ensuring operational safety.
Petrochemical & Chemical Processing
CF8M stainless steel and duplex alloy cast valves resist attack from aggressive acids, solvents, and process chemicals. Globe valves are specified for flow control in reactor cooling loops, while ball valves provide emergency isolation of hazardous chemical streams.
Water & Wastewater Treatment
Municipal plants and industrial utilities deploy large-bore WCB cast steel gate valves for mainline isolation, as well as check valves for pump discharge lines. Their size range up to 60” makes them ideal for high-capacity distribution systems.
Mining & Minerals
Slurry pipelines and mineral processing plants require erosion-resistant valves. Hard-facing and duplex materials are used to mitigate wear from abrasive particles in process streams.
Pulp & Paper
Cast steel valves in bleaching and digesting operations manage corrosive chemicals at elevated temperatures. Stainless and specialty alloys are ideal for long-term service life.
HVAC & Industrial Utilities
Large facilities and district heating/cooling systems use cast steel globe and gate valves for chilled water and steam distribution, thus ensuring reliable thermal management.
Marine & Offshore Applications
Offshore production platforms, LNG carriers, and FPSOs demand LCC and CF8M valves that retain toughness in cryogenic or saline environments.
QRC Full Product Range
Beyond product supply, QRC provides engineering consultation, application-specific valve selection, and after-sales support. QRC also provides other valve solutions in cast steel, stainless steel, and exotic alloys, ensuring coverage across all industries and service conditions.
Our inventory covers gate, globe, check, and specialty valve options across leading brands. Thus, ensuring clients receive solutions optimized for both performance and lifecycle cost. Explore the full range here: QRC Products.
Cast steel valves remain a cornerstone of industrial valve technology, delivering strength, leak-tight reliability, and adaptability across critical sectors. For expert guidance on selecting the right valve for your operation, contact QRC’s technical team for more information.


Recent Comments