Valve Maintenance
Valves regulate the gases, liquids, and slurries flows in various mechanical applications. They maintain the process control and safety of industrial systems and equipment. However, valves might experience wear, tear, corrosion, or residue build-up over time, leading to leaks, blockages, or failure. Therefore, valve maintenance becomes essential for any facility operation.
Why Do Valves Need Maintenance?
Operational efficiency, longevity, and workplace safety provide three major reasons for valve maintenance.
Regular valve maintenance ensures the valve accurately controls the flow rate, direction, and pressure level. This accuracy ensures efficiency of any plant or equipment, such as petroleum refineries, wastewater treatment plants, and marine hardware. Next, it minimizes the risk of sudden problems in piping systems and reduces unexpected downtime.
Maintenance directly contributes to valve longevity since it prevents premature wear and tear. As a result, you can avoid major repairs and replacement expenses.
Imagine the havoc that a gasoline leak in a refinery would cause. Avoiding these incidents necessitates proactive maintenance to prevent leaks, ruptures, or catastrophic failures of piping systems under pressure.
Much of valve maintenance is predicated on accessibility. Valves are usually set inside the flow path of an active process and removal necessitates the unbolting of flanges and diversion of cessation of a fluid’s flow path. Such an action may not be desirable or possible. Oftentimes, visual inspection may be the only available option.
Gate Valve Maintenance
A gate valve opens the flow in a piping system by lifting a rectangular or round gate in the path of the fluid. It is commonly found in applications requiring a free flow or minimal restriction.
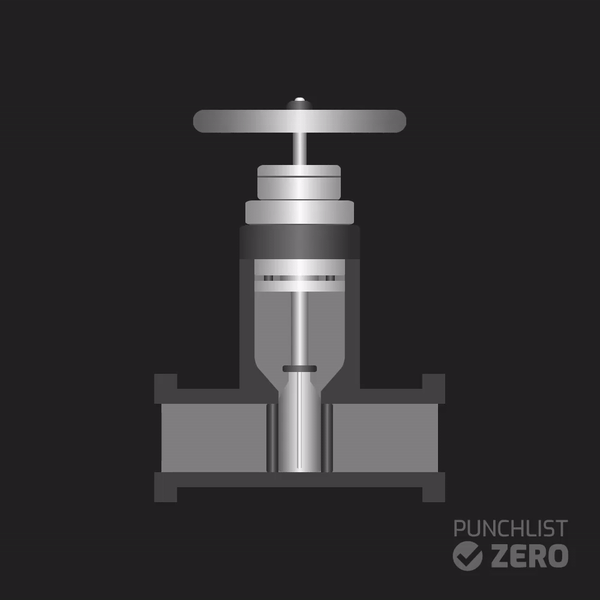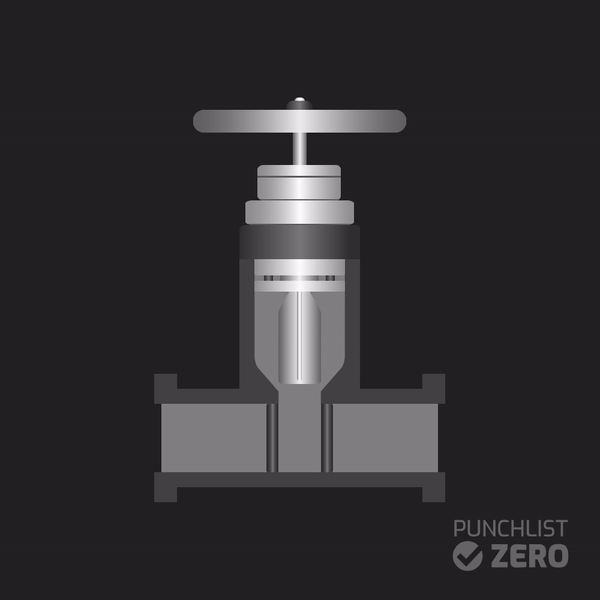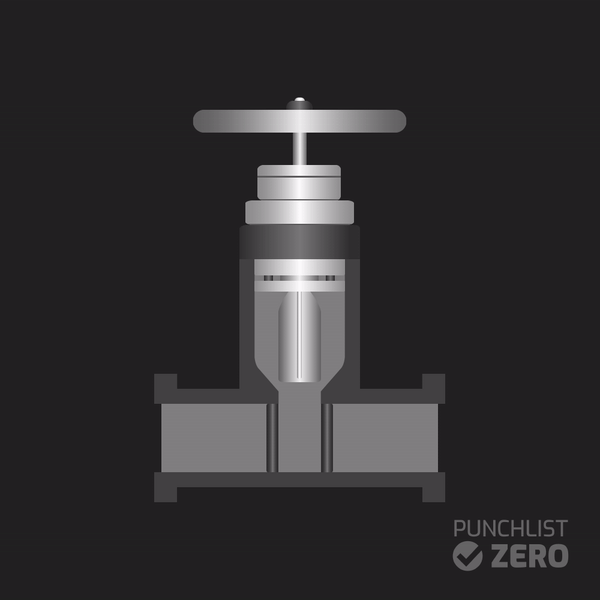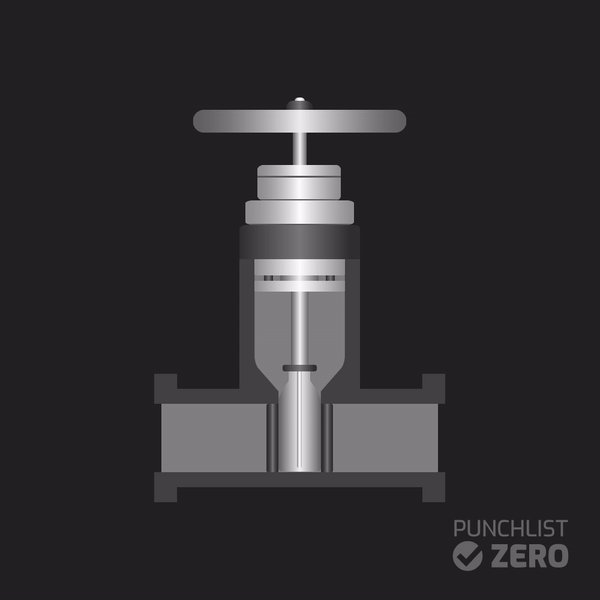
A standard gate valve maintenance process includes the following steps:
-
- A thorough visual inspection for any signs of wear, corrosion, or leaks.
-
- Checking bolt integrity and ensuring correct valve alignment.
-
- Based on the manufacturer’s guidelines, lubricate the valve stem and moving parts.
-
- Identify whether there is any sealing surface damage and debris or not. If yes, assess the required disassembly for cleaning or repair.
-
- Clean all gate valve components with appropriate tools to remove dirt, rust, or scale. Check the valve seat and gate for erosion, damage, repair, or replacement parts.
Furthermore, gate valves might involve a packing gland in some applications, like chemical processing plants. If so, inspect for wear or leakage. Then, adjust or replace the packing material accordingly.
Globe Valve Maintenance
Like every other valve, the globe valve demands regular inspection to identify the necessity of maintenance. It could be anything from inspection of wear & tear, weeping around the valve body, or leakage. On the other hand, regular maintenance includes adjusting the packing gland bolts, lubrication, checking valve seats and discs, etc.
| Issues in Operation | Potential Causes | Maintenance or Repair Action | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flow Leakage | Worn or damaged packing, loose bonnet bolts, or improper seating | Replace packing, tighten bonnet bolts, and reseat valve | Aggressive slurry transport |
| Stiff Operation | Sediment build-up, stem corrosion, and lack of lubrication | Clean and lubricate moving parts & valves, and replace if any part is corroded | Water treatment plants |
| Incomplete Closure | Wear on disc or seat and misalignment | Resurface or replace seat/disc and realign valve components | Typical with valves regulating high-pressure steam. |
| Corrosion/Damage | Corrosion due to harsh fluids or environment, and mechanical damage | Replace if parts are damaged, apply protective coatings | Valves exposed to saline environments, such as marine applications. |
| Abnormal Noise | Loose internal components, cavitation, flow turbulence | Adjust internal components, check flow rates, and look for cavitation | Noise issues in valves controlling heating or cooling flow in an HVAC system. |
Gate Valve Issues and Troubleshooting
A check valve permits passage in one direction while automatically preventing reverse flow. For example, a check valve automatically closes against excessive downstream pressure for the uni-directional flow of gases in oil refinery piping.
Periodic maintenance includes cleaning, lubrication, and testing flow and back-flow pressure.
Here are troubleshooting actions to ensure optimal performance during operation:
-
- Check that the installation aligns with the flow and ensure a recommended pressure to activate the valve.
-
- Visually verify that no obstructions exist within the valve, such as sediment, residue, or debris.
-
- Examine the valve sealing areas for wear or damage to check valve closing issues.
-
- If any parts (disc, seat, spring, hinge pin, etc.) have noticeable wear or damage, replace them.
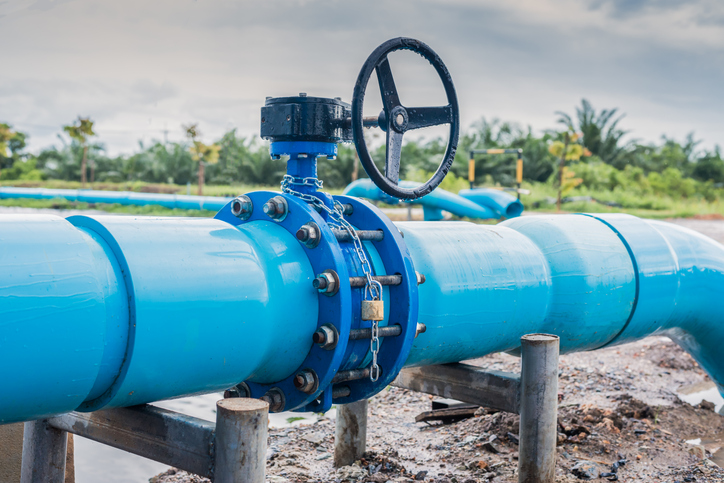
Butterfly Valve Maintenance
These valves can range from fully open to fully closed, regulating, or throttling the fluid flow in large pipes with limited space conditions. Butterfly valves are especially popular in high-performance areas like energy plant equipment and HVAC systems. Meanwhile, a lack of valve maintenance can lower the downtimes or even equipment failure.

Regular maintenance of a butterfly valve includes the following:
-
- Cleaning and lubrication
-
- Seal and gasket replacement
-
- Verification of torque required for operation.
-
- Checking the hydraulic or pneumatic pressures and electrical system associated with the actuator.
Despite regular maintenance, a butterfly valve might face sudden operational issues like leakage, sticking, binding, insufficient flow control, and excessive torque. Removing the obstruction, replacing the worn parts, correcting adjustments on parameters, and fixing alignment solves these problems. A savvy operator should fix the problem based on the root causes.
Plug Valve Maintenance
A plug valve controls the fluid flow with a cylindrical or conically tapered “plug”. This plug rotates and regulates the flow through the valve. Subsequently, plug valves require periodic maintenance to maintain functionality and optimal performance.
Here are the plug valve activities:
-
- Clean the plug valve components and apply correct lubrication fittings like giant button heads or lube stick injection.
-
- Consequently, apply lube to the plug and other moving parts.
-
- Monitor the wear and tear on parts. Then repair or replace accordingly.
-
- Check the condition of the sealant and how much pressure it bears.
However, several other troubleshooting actions are necessary to handle potential plug valve issues in any system or equipment.
| Specific Issue | Cause | Troubleshooting |
|---|---|---|
| Sticking or Hard Operation | Debris, lack of lubrication, and corrosion | Clean the valve internals, lubricate, and replace corroded parts |
| Leakage From the Valve | Worn seals, incorrect plug alignment, and valve seat erosion | Replace seals/valve seat and realign plug |
| The Problem in Complete Shutoff | Misaligned/worn plug, worn valve seat, and debris obstruction | Repair/replace the plug and valve seat, clean debris, repair/replace valve seat |
| Excessive Wear | Rapid cycling, abrasive flow, and unsuitable valve sizing | Review application specifications, use wear-resistant materials, and maintain proper sizing |
Plug Valve Issues and Troubleshooting
Ball Valve Maintenance
A rotating spherical ball with a bore inside regulates the flow in a ball valve. Meanwhile, the shaft connected to this ball and seat controls the ball’s movement.
General ball valve maintenance includes:
-
- Inspection of wear, tear, corrosion, and other damages.
-
- Ensuring accurate positioning and alignment.
-
- Performing pressure testing to identify the leakage.
On the other hand, the following are the potential problems that might arise during the continuous operation of ball valves.
| Issues | Causes | Troubleshooting |
|---|---|---|
| Leakage | Worn stem seals or O-rings, corrosion, or damage | Replace seals/O-rings, tighten packing gland |
| Ball Damage | Corrosion or physical damage | Replace the ball, ensure the ball is made with corrosion-resistant materials |
| Improper Ball Alignment | Misalignment of the ball within the valve | Set the correct ball alignment |
| Handle Breakage or Wear | Physical wear or improper handling | Change handle, ensure proper attachment |
| Excessive Torque Requirements | Unsuitable sizing, internal obstructions | Check valve size, clear obstructions |
Ball Valve Issues and Troubleshooting


